Orbis Overview
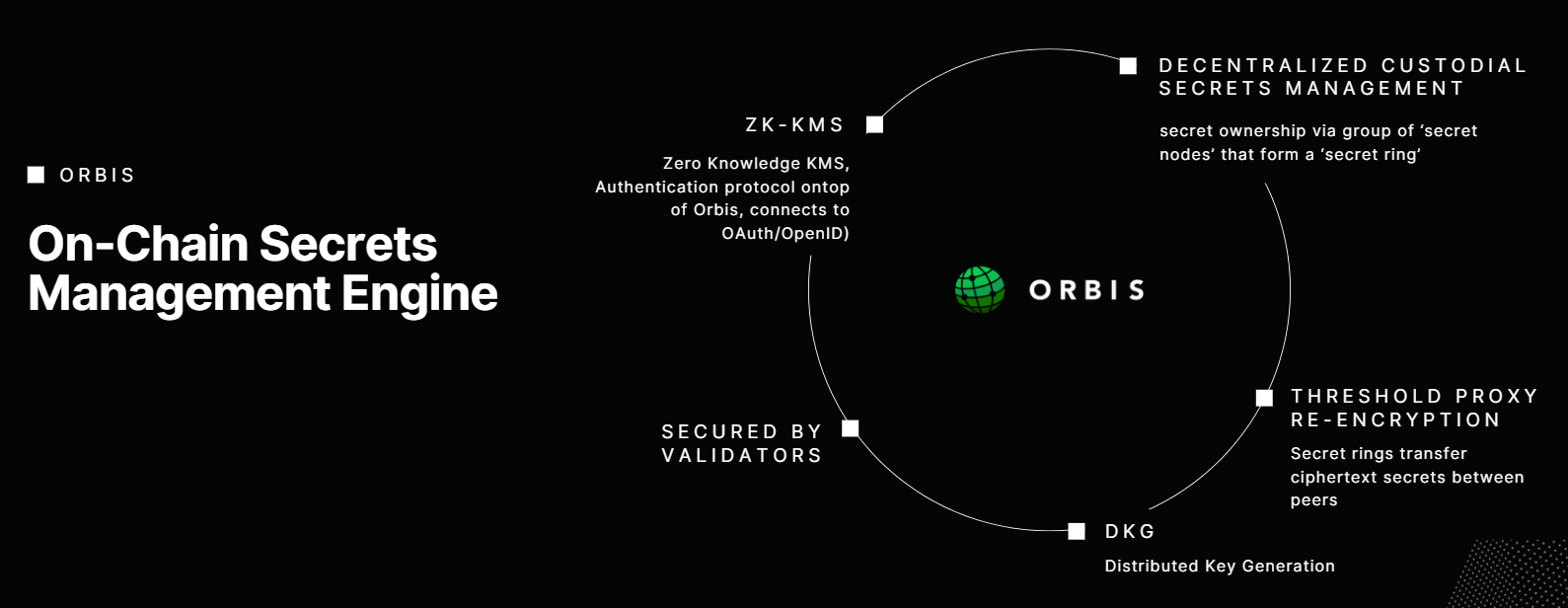
Orbis is a decentralized Secrets Management engine powered by Threshold-Proxy ReEncryption and Multi-Party Computation to enable trustless system to manage and share application and user secrets. Application and user secrets can be anything from encryption keys, API tokens, to general small sized messages. This is comparable to other Secrets Management systems like Hashicorp Vault but without a single centralized entity.
How it works
Deployments of Orbis are called Secret Rings which are initialized by a group of nodes, which collectively agree on some starting Manifest. These manifest define the initial parameters, such as which kind of authentication/authorization, Proxy Re-encryption, Distributed Key Generation (DKG) algorithms, bulletin protocol, etc are used.
Once the manifest is created, Secret Ring nodes will start their initial DKG ceremony, which will generate a shared keypair maintained by the nodes, where each node has a share of the private key, and in aggregrate represent a single public key. When a threshold number of nodes (defined by the chosen parameters in the Manifest) collaborate, they are able to execute various kinds of cryptograhic operations.
Once a Ring is fully configured and initialized users that want to store secrets will encrypt their secret S to the rings aggregate public key Pk, Se = Enc(S, Pk). They then send Se to any of the Orbis nodes along with the Authorization Context that determines how the configured authorization system processes requests (which is dependant on the authz parameter of the Manifest), as a StoreSecret request. Finally the receiving node will broadcast the request to the Rings' bulletin protocol to sync with the rest of the nodes.
The Root Ring is a special deployment Orbis Ring that is a public permissionless service provided by the same infrastructure nodes as the SourceHub publicly hosted service. This ensures there is a single public Source stack deployment that developers can use along side their DefraDB nodes.